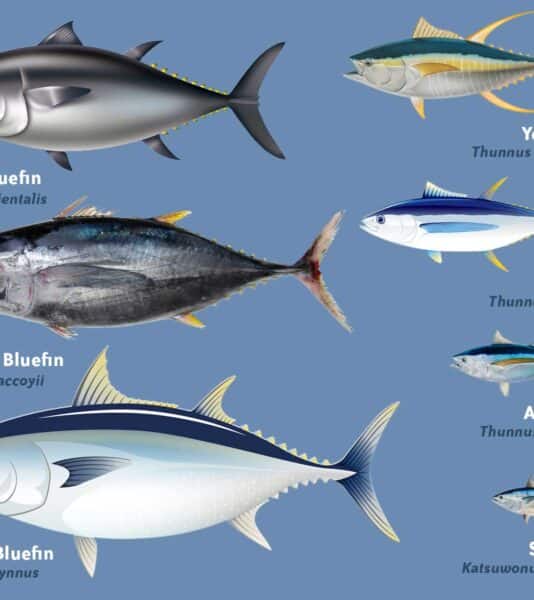
Tuna ranks among the top three most popular species year after year in North America. Its popularity is no surprise, as tuna can be found in all the world’s oceans and is enjoyed both fresh and canned.
Did you know there are 15 species of tuna? The seven listed below are considered main or major in the commercial tuna market. The remaining eight are still caught commercially and recreationally but not nearly in the volume as the main seven.
| 7 Main Tuna Species | 8 Minor Tuna Species |
|---|---|
| Albacore | Black Skipjack |
| Bigeye | Blackfin |
| Atlantic Bluefin | Bullet |
| Pacific Bluefin | Frigate |
| Southern Bluefin | Kawakawa |
| Yellowfin | Longtail or Tongol |
| Skipjack | Little tunny |
| Slender |
Let’s see how they measure up:
| Tuna Species | Maximum Weight | Maximum Length |
|---|---|---|
| Albacore Tuna | 90 lbs | 5 ft |
| Bigeye Tuna | 400 lbs | 8 ft |
| Atlantic Bluefin Tuna | 2,000 lbs | 10.5 ft |
| Pacific Bluefin Tuna | 990 lbs | 10 ft |
| Southern Bluefin Tuna | 1,210 lbs | 5 ft |
| Yellowfin Tuna | 400 lb | 7 ft |
| Skipjack Tuna | 75 lbs | 3.5 ft |
These figures are estimates and vary based on factors such as age, location, and the individual fish. But it gives you an idea of the dramatic differences. Look how much bigger an Atlantic Bluefin is than a Skipjack!
7 MAIN SPECIES OF TUNA
Now we profile the seven major species of tuna in more detail.
ALBACORE
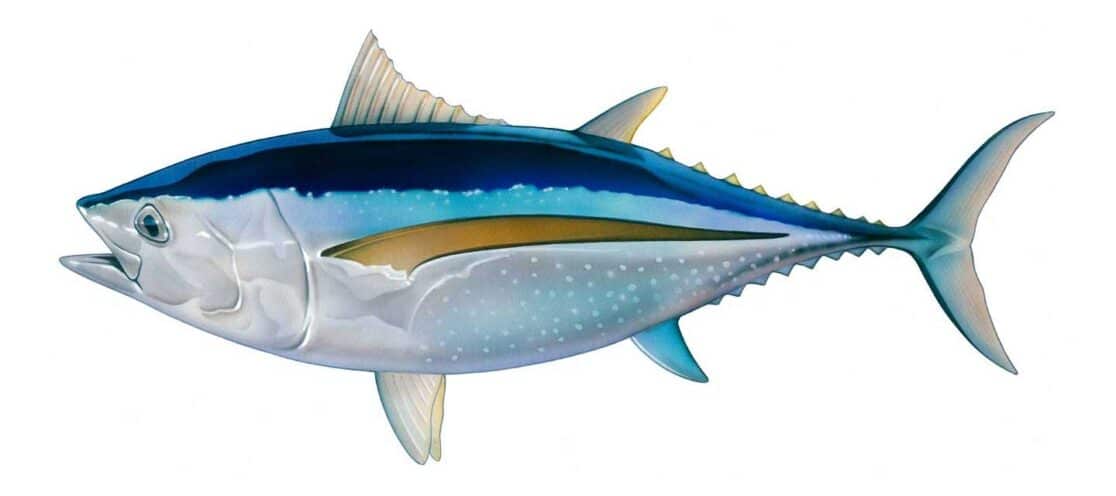
Distinguishing Features:
- Elongate, fusiform body with a conical snout
- Large eyes
- Remarkably long pectoral fins
- Deep blue dorsally and shades of silvery white ventrally
- Unique diet preference for cephalopods (such as octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish)
Taste and Texture: Milder flavor than most tunas and meaty texture makes it suitable for various dishes, from salads to casseroles.
Habitat: Found in temperate and tropical waters worldwide, often inhabiting deep offshore areas.
Latin Name:Thunnus alalunga
BIGEYE
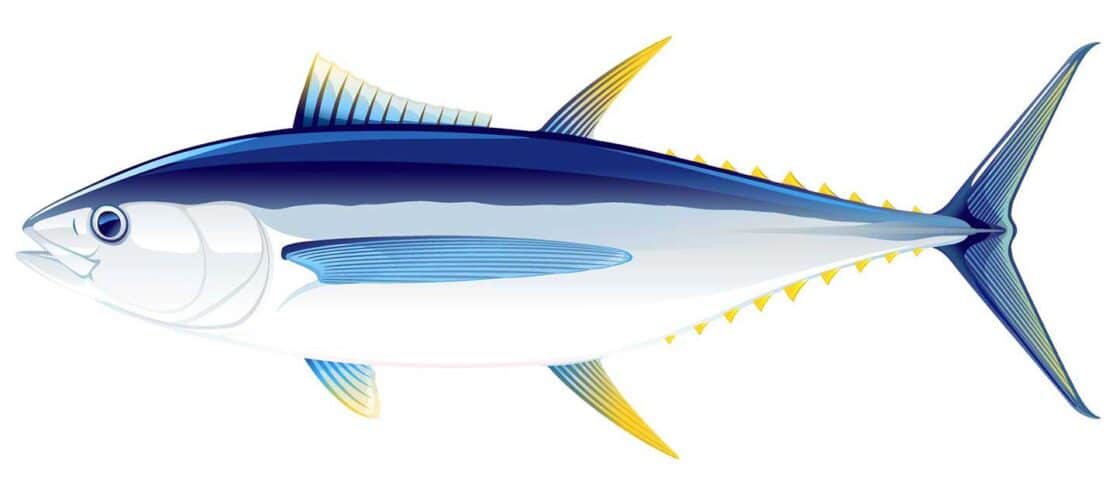
Distinguishing Features:
- Large, deep-bodied, streamlined fish
- Large head and eyes
- Very long pectoral fins
- 13 or 14 dorsal spines
- Unique physiology allowing them to forage in deeper, colder waters
Taste and Texture: Rich, sweet flavor with a clean, less “fishy” profile. The texture is firm and tender, ideal for searing or raw preparations.
Habitat: Prefers deeper, warmer waters in tropical and subtropical regions, often near islands or seamounts.
Latin Name: Thunnus obesus
ATLANTIC BLUEFIN
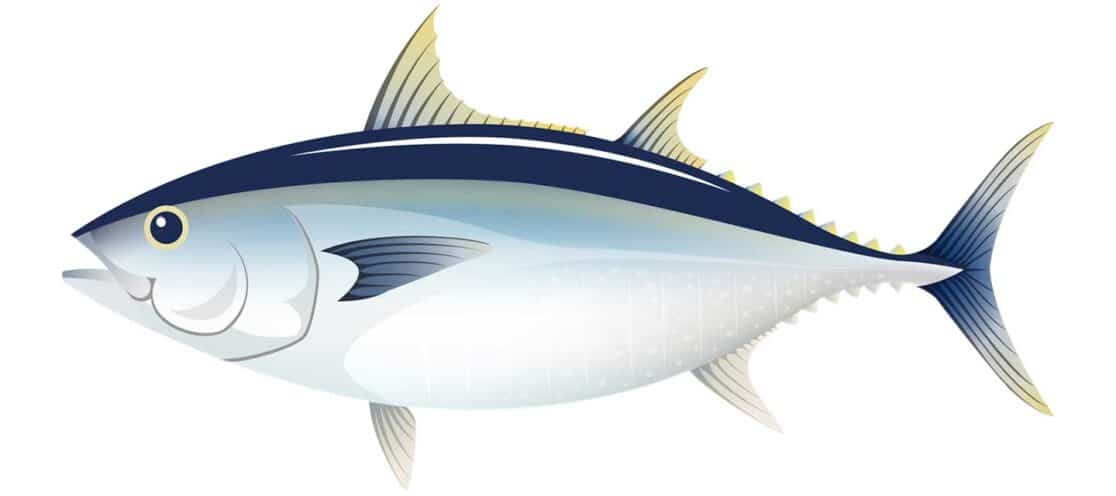

Distinguishing Features:
- Distinguishing Features:
- Dark blue coloring on the top and a gray or shimmering white coloring below
- Gold shimmer to the entire body
- Dark red meat
- Tips of pectoral fins do not reach the front of the second dorsal fin
Taste and Texture: Mild, buttery, and savory flavor, with a subtle sweetness. The texture is firm and smooth, often enjoyed raw in sushi and sashimi.
Habitat: Occurs in the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, migrating long distances and often found in cooler waters. The Mediterranean is a significant spawning ground for this species.
Latin Name: Thunnus thynnus
PACIFIC BLUEFIN
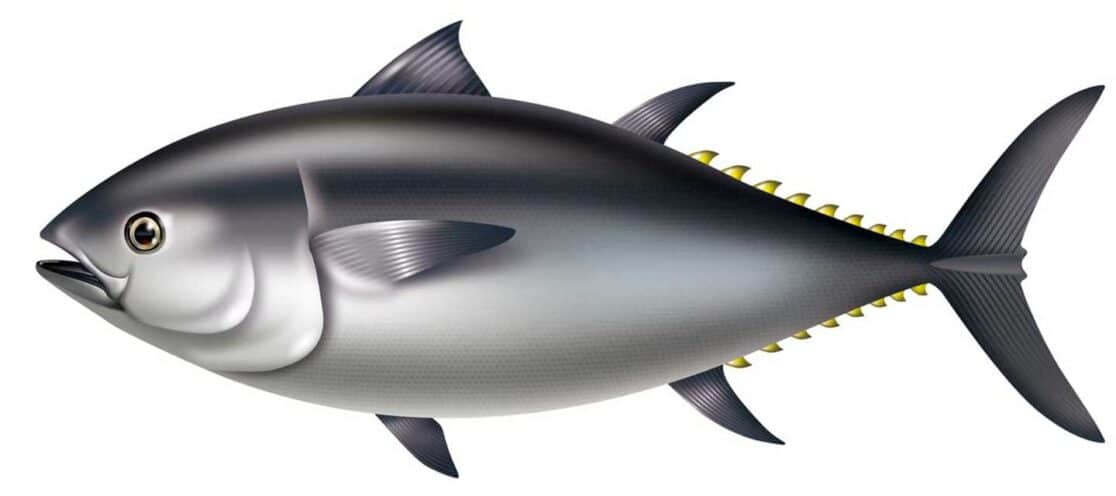
Distinguishing Features:
- Black or dark blue dorsal sides with a grayish-green iridescence
- Small eyes compared to other tuna species
- Pectoral fin tips do not reach the front of the second dorsal fin
Taste and Texture: Pacific Bluefin has a distinct, succulent flavor with an oceanic essence. Its texture is firm and slightly chewy.
Habitat: As its name implies, it is found in the Pacific Ocean, ranging from the western Pacific to the eastern Pacific, and known for long-distance migrations.
Latin Name: Thunnus orientalis
SOUTHERN BLUEFIN
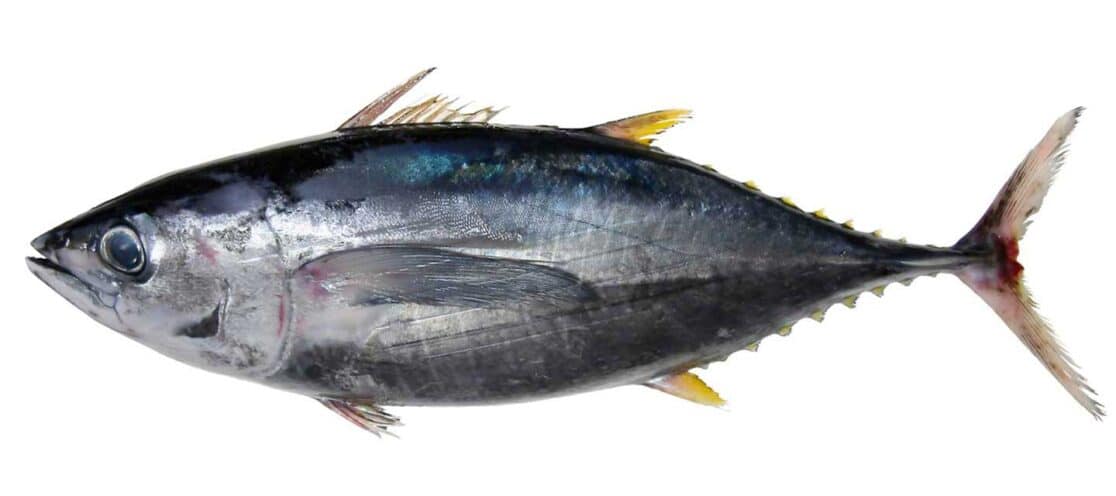

Distinguishing Features:
- Found in open southern Hemisphere waters mainly between 30°S and 50°S
- Maintains body core temperature up to 10°C above ambient temperature
- Unique respiratory and circulatory adaptations for high metabolic demand
Taste and Texture: Southern Bluefin is buttery, smooth, and has a melt-in-your-mouth tender feel because it is marbled with fat.
Habitat: Inhabits the southern hemisphere’s temperate and cold waters, often found in the open ocean.
Latin Name: Thunnus maccoyii
YELLOWFIN
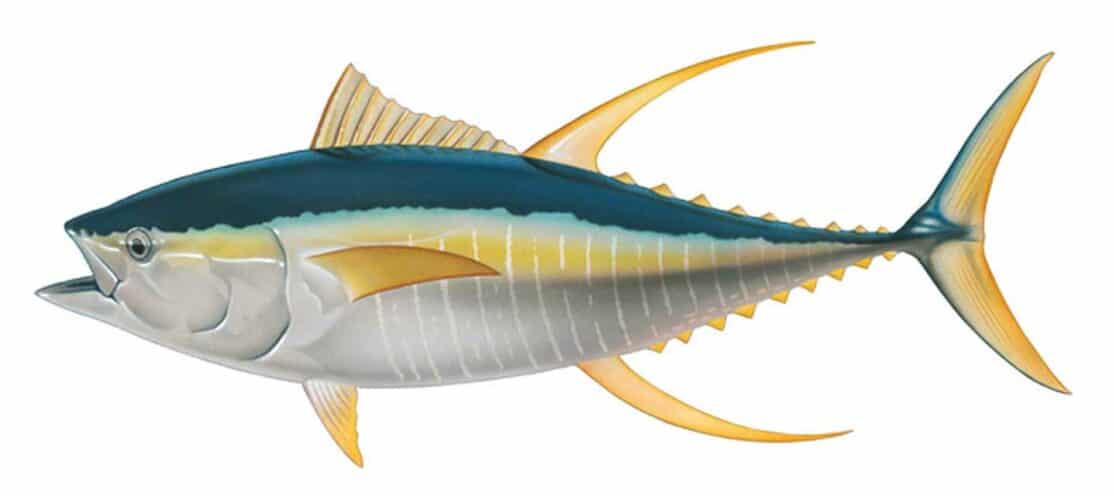

Distinguishing Features:
- A yellow dorsal fin and yellow sides
- Long second dorsal fin
- Dark blue-black back and silver-white belly
- Moderately large eyes
- Yellow finlets on the tail
Taste and Texture: Yellowfin has a bolder flavor and softer texture than albacore. This makes it ideal where a richer tuna taste is desired, such as sandwiches or pasta dishes.
Habitat: Prefers tropical and subtropical waters worldwide, often near the surface or associated with floating objects. It can be found in the Mediterranean, mainly in the eastern basin and often associated with warm currents.
Latin Name: Thunnus albacares
SKIPJACK
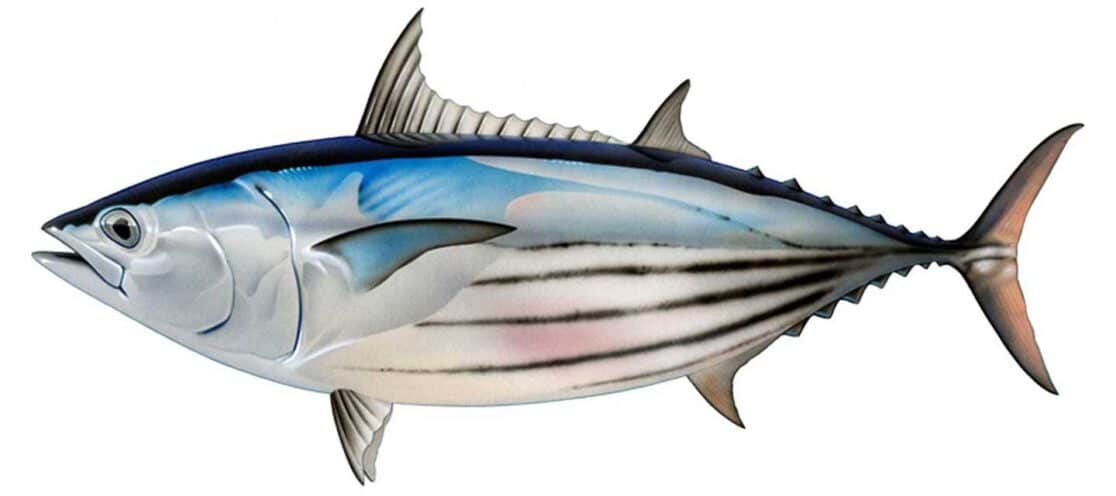
Distinguishing Features:
- Iridescent blue with black markings on the back
- Bullet-shaped body
- Tender meat, often used for canning
- Smaller size compared to other tuna species
Taste and Texture: Skipjack tuna has a stronger, fishier flavor and a softer texture.
Habitat: Found in tropical and warm temperate waters worldwide, often in large schools near the surface.
Latin Name: Katsuwonus pelamis
NUTRITION AND HEALTH BENEFITS
Incorporating all types of tuna into your diet can provide a tasty and nutritious boost while potentially lowering the risk of various health conditions. Let’s delve into the nutritional value of tuna and its potential health benefits:
Nutritional Value
- Vitamin B12: Tuna is an excellent source of vitamin B12, a crucial nutrient needed for DNA synthesis and the formation of new red blood cells. Adequate B12 intake helps prevent anemia and supports overall health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Tuna is rich in omega-3s, which play a vital role in heart health. These fatty acids can help reduce inflammation, lower levels of harmful LDL cholesterol, and maintain healthy arteries. Regular consumption of omega-3s is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks.
- Vitamin D: Just 3 ounces of canned tuna provide up to 50% of the recommended daily level of vitamin D. Vitamin D is essential for bone health, immune system function, and optimal growth in children.
Health Benefits
- Heart Disease: The omega-3s in tuna help maintain a healthy balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids, reducing the risk of heart disease. By keeping arteries clear and supporting cardiovascular health, tuna consumption contributes to overall well-being. Tuna is also naturally low in sodium and low-sodium or sodium-free options are available for canned tuna.
- Cancer Prevention: Tuna’s omega-3 fatty acids are believed to inhibit tumor cell growth and reduce inflammation. Chronic inflammation is associated with several types of cancer, making tuna a valuable addition to a cancer-preventive diet.
- Weight Management: Tuna is a lean protein, filling and satisfying without excess calories. Adolescents who regularly consume lean fish like tuna have been shown to lose more weight than those who don’t.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is tuna fish good for your body?
Yes, tuna fish is good for your body due to its heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids and rich nutrient content. According to the FDA, the mercury present in tuna fish is not a risk for most people. However, the FDA recommends that children ages 1-11 and women who are pregnant or breastfeeding limit their tuna intake to no more than one serving (4 ounces) per week.
Is tuna the healthiest fish?
When it comes to healthy fish options, tuna is a great choice. It contains beneficial nutrients such as omega-3s and is a lean protein, so it’s filling and satisfying without bringing excess calories.
Why is tuna fish so expensive?
Certain types of tuna, such as bluefin are expensive due to limited supply. But canned tuna is affordable because it primarily comes from smaller tuna varieties that grow fast and are abundant. Plus, the canning process preserves tuna, extends its shelf life, and makes it cost-effective for mass production.
Sources:
https://www.iss-foundation.org/tuna-stocks-and-management/tuna-fishing/tuna-species
https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/fish/big-tunas
https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/find-species

WHERE TO BUY
Use our product locator to find the perfect salmon, tuna, crab or other seafood products from Chicken of the Sea.
- Products
- Choose Your Product
-
- Wild Caught Light Tuna in Spring Water Packet
- Wild Caught Light Tuna Packet, Lemon Garlic
- Wild Caught Light Tuna Packet, Sweet & Spicy
- Wild Caught Light Tuna Packet, Dill Tuna Salad
- Wild Caught Alaskan Pink Salmon in Spring Water Packet
- Wild Caught Alaskan Pink Salmon in Spring Water Packet, Low Sodium
- Wild Caught Alaskan Pink Salmon Packet, Everything Bagel Seasoning
- Wild Caught Alaskan Pink Salmon Packet, Lemon Pepper
- Wild Caught Smoked Alaskan Pink Salmon Packet, Maple Smokehouse Flavor
- Wild Caught Smoked Alaskan Pink Salmon Packet, Natural Wood Smoke
- Wild Caught Albacore Tuna in Spring Water Packet
- Wild Caught Chunk Light Tuna in Water
- Wild Caught Chunk Light Tuna in Water, 25% Less Sodium
- Wild Caught Chunk Light Tuna in Oil
- Wild Caught Solid White Premium Albacore Tuna in Water
- Wild Caught Solid White Premium Albacore Tuna in Oil
- Wild Caught Solid White Premium Albacore Tuna in Water, Low Sodium
- Wild Caught Alaskan Pink Salmon, Skinless & Boneless
- Wild Caught Alaskan Pink Salmon, 25% Less Sodium
- Wild Caught Sardines in Water
- Wild Caught Sardines in Olive Oil
- Whole Oysters
- Wild Caught Sardines in Oil, Lightly Smoked
- Imitation Crabmeat in Brine Packet
- Wild Caught Lump Crabmeat
- Wild Caught White Crabmeat
- Smoked Baby Clams in Oil Packet
- Crab Cakes
- Wild Caught Chub Mackerel in Brine
- Wild Caught Chopped Clams
- Whole Baby Clams
- Wild Caught Sardines in Louisiana Hot Sauce Packet
- Wild Caught Sardines in Mustard Sauce
- Wild Caught Mackerel Fillet in Oil Packet
- Wild Caught Mackerel in Oil Packet
- Wild Caught Sardines in Louisiana Hot Sauce
- Wild Caught Solid White Premium Albacore Tuna in Water, No Salt Added
- Perfectly Crisp Shrimp
- Crispy Stuffed Shrimp – Creamy Garlic & Spinach
- Wild Caught Chunk White Albacore Tuna in Water
- Crispy Stuffed Shrimp – Creamy Jalapeno
- Wild Caught Chunk White Albacore Tuna in Water, Low Sodium
- Wild Caught Chunk Yellowfin Tuna in Vegetable Oil
- Infusions Basil Tuna
- Infusions Lemon & Thyme Tuna
- Smoked Oysters in Oil Packet
- Infusions Thai Chili Tuna
- Fancy Smoked Oysters in Oil
- Wild Caught Sardines in Oil with Natural Smoke Flavor Packet
- Infusions Garlic & Herb Tuna
- Infusions Cracked Black Pepper Tuna
- To-Go Cups – Chunk Light Tuna in Water
- Wild Caught Sardines, Mediterranean Style
- Wild Caught Sardines in Lemon Sauce
- Wild Caught Alaskan Pink Salmon, Traditional Style
- Wild Caught Alaskan Sockeye Red Salmon, Traditional Style
- Wild Caught Pink Salmon with Lemon & Chive
- Blue Swimming Crab – Lump
- Blue Swimming Crab – Super Lump
- Blue Swimming Crab – Jumbo Lump
- Blue Swimming Crab – Backfin
- Blue Swimming Crab – Colossal
- Blue Swimming Crab – Claw
- Blue Swimming Crab – Special
- Raw Peeled & Deveined Tail-On Shrimp
- Raw Peeled & Deveined Tail-Off Shrimp
- Raw Shell On, Easy to Peel Shrimp
- Easy Grillers Uncooked Shrimp
- Cooked Peeled & Deveined Tail-On Shrimp
- Cooked Peeled & Deveined Tail-Off Shrimp
- Crispy Stuffed Shrimp – Creamy Wonton